Each character is assigned its own identification number for use on a PC, and this number is referred to as the character code. Different international standards and the standards of specific countries have assigned different codes to the same character so a given character has a Unicode® number, a Shift_JIS number, a JIS number, etc.

Font files are provided in the form of character sets which bring together multiple characters.
There are several types of character sets, including Microsoft Corporation's Windows® Codepage (CP), ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards, JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards), ARIB (Association of Radio Industries and Businesses) standards, GB (Chinese national standards), etc. The types of characters and the number of characters included differ between character sets.
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| CP932 | JIS X 0201(Half-width) | 158 |
| JIS X 0208(Non-Kanji) | 616 | |
| JIS X 0208 Kanji Level 1 | 2,965 | |
| JIS X 0208 Kanji Level 2 | 3,390 | |
| NEC special | 89 | |
| IBM®extension | 374 | |
| NEC selected IBM®extension | 0 | |
| Total | 7,592 | |
| JIS X 0208-1990 | JIS X 0208(Non-Kanji) | 577 |
| JIS X 0208 Kanji Level 1 | 2,965 | |
| JIS X 0208 Kanji Level 2 | 3,390 | |
| Total | 6,932 | |
| CP932+JIS X 0213:2004 | JIS X 0201(Half-width) | 158 |
| JIS X 0208(Non-Kanji) | 616 | |
| JIS X 0208 Kanji Level 1 | 2,965 | |
| JIS X 0208 Kanji Level 2 | 3,390 | |
| NEC special | 89 | |
| IBM®extension | 374 | |
| NEC selected IBM®extension | 0 | |
| JIS X 0213 Non-Kanji | 575 | |
| JIS X 0213 Kanji Level 3 | 1,071 | |
| JIS X 0213 Kanji Level 4 | 2,348 | |
| Total | 11,586 | |
| ARIB STD-B24 | JIS X 0201(Half-width) | 158 |
| JIS X 0208(Non-Kanji) | 577 | |
| JIS X 0208 Kanji Level 1 | 2,965 | |
| JIS X 0208 Kanji Level 2 | 3,390 | |
| Additional code | 399 | |
| Additional kanji | 137 | |
| Total | 7,626 |
About ARIB and ARIB-compatible fonts
ARIB (Association of Radio Industries and Businesses) is an incorporated Japanese industry association which enacts standards concerning digital broadcasts and cellular telephones in Japan. Digital broadcasts are supposed to use characters compatible with ARIB standards.
At Ricoh, we provide fonts compatible with ARIB STD-B24 (a data broadcasting encoding system and transmission system for digital broadcasting). This standard applies to broadcasting systems up to Hi-Vision HDTV.

Used on Chinese mainland, etc.
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| GB18030-2005(Mandatory part) | 1 Byte Half-width ASCII | 95 |
| 2 Byte/Section1(Non-Kanji) | 728 | |
| 2 Byte/Section5(Non-Kanji) | 166 | |
| 2 Byte/Section2(Non-Kanji) | 6,763 | |
| 2 Byte/Section3 (Non-Kanji) | 6,080 | |
| 2 Byte/Section4(Kanji) | 8,160 | |
| 4 Byte (Kanji) | 6,530 | |
| Total | 28,522 |
GB (GB standards)
China has national standards known as GB (GB standards), which are approved and issued by the Standardization Administration of China (SAC). The name "GB" comes from the first letters of the Chinese term for "national standards," which is "Guójiā Biāozhǔn."
Simplified Chinese character certification
When simplified Chinese characters are included on products used in China, for bitmap fonts companies are supposed to use standard fonts owned by the Chinese government and for outline fonts they are supposed to use fonts that have received Chinese government certification.
At Ricoh, we provide outline fonts (TrueType Font/RT Font) that have passed the conformity assessment carried out by the Chinese government's official certification organization (Conformance Test Center For Information Technology Standards: CTCITS). If you are searching for the standard bitmap fonts owned by the Chinese government, please inquire using the free consultation function.
Used in Taiwan, etc.
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| CP950 | Half-width characters | 95 |
| Big5(Non-Kanji) | 408 | |
| Big5 1st Standard Collection | 5,399 | |
| Big5 2nd Standard Collection | 7,652 | |
| E-TEN | 7 | |
| Border fragment | 25 | |
| Graphic pattern | 1 | |
| Euro symbol | 1 | |
| Total | 13,588 |
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| KS X 1001:2004(without hanja) + KS X 1003-1993 |
Half-width characters | 95 |
| Master | 94 | |
| Symbol | 895 | |
| Hangul | 2,350 | |
| Total | 3,434 |
| Region / Language | Character Set | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| Western Europe | ISO8859-1 | 191 |
| CP1252 | 218 | |
| Central Europe | ISO8859-2 | 191 |
| CP1250 | 218 | |
| Southern Europe | ISO8859-3 | 184 |
| Northern Europe | ISO8859-4 | 191 |
| Cyrillic (Russian, etc.) | ISO8859-5 | 191 |
| CP1251 | 223 | |
| Greek | ISO8859-7 | 188 |
| CP1253 | 206 | |
| Turkish | ISO8859-9 | 191 |
| CP1254 | 216 | |
| North Germanic Languages | ISO8859-10 | 191 |
| Baltic | ISO8859-13 | 191 |
| CP1257 | 211 | |
| Celtic | ISO8859-14 | 191 |
[ Character set support status by language ]
| ISO8859 | CP | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Languages | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 1250 | 1251 | 1252 | 1253 | 1257 |
| Afrikaans | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||||
| Albanian | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||
| Arabic | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Baltic language family | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Basque | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Belarusian | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Bosnian | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Breton | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Bulgarian | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Catalan | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Cornish (Celtic) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||
| Croatian | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||||
| Czech | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Danish | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||
| Dutch | △[1] | △[1] | △[1] | △[1] | ||||||||||||||||
| English | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Esperanto | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Estonian | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||
| Euro symbol [€(U+20AC)] | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Faroese | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||
| Finnish | △ | ○ | △ | ○ | ○ | △ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||
| French | △ | △ | △ | △ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||
| Frisian | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||
| Gaelic (Isle of Man Gaelic) | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Galician | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| German | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||
| Greenlandic | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||
| Hebrew | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Hungarian | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||||
| Icelandic | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||
| Indonesian | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||||
| Ireland Gaelic (new spelling standard) | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||
| Ireland Gaelic (old spelling standard) | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Irish | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||||
| Italian | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||
| Kurdish | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Latin | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Latvian | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||||
| Lithuanian | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||
| Luxembourgish | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Macedonian | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Maltese | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Modern Greek | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| North Germanic language family | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Norwegian | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||
| Polish | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Portuguese | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||
| Rhaeto-Romance | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Rumanian | △[2] | ○ | △[2] | |||||||||||||||||
| Russian | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sami | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scotland Gaelic | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Serbian | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Slovak | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Slovene | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Sorbian | ○ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Spanish | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||
| Swahili | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||||||
| Swedish | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||||||||||||
| Thai | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Turkish | △ | ○ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ukrainian | △ | △ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Welsh | ○ | |||||||||||||||||||
[Legend]
○:Fully supported.
△:Almost fully supported, but there are some characters which are not supported.
[1]:[IJ(U+0132)/ij(U+0133)] missing
[2]:[Ș(U+0218)/ș(U+0219)] and [Ț(U+021A)/ț(U+021B)] (characters with comma accent) are missing, but those characters were previously unified with [Ș(U+015E)/ș(U+015F)] and [Ț(U+0162)/ț(U+0163)] (characters with cedilla).
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| CP1256+137characters | CP1256 Regulated character | 223 |
| CP1256 Non-regulated character | 137 | |
| Total | 360 |
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| CP1255+82characters | CP1255 Regulated character | 200 |
| CP1255 Non-regulated character | 82 | |
| Total | 282 |
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| CP874 | CP874 Regulated character | 192 |
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| CP1258+104characters | CP1258 Regulated character | 214 |
| CP1258 Non-regulated character | 104 | |
| Total | 318 |
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| Unicode Devanagari defined characters | Unicode Devanagari defined characters | 155 |
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) is technology used to read handwritten or printed characters with an image scanner or digital camera and then convert the characters to character codes that can be used by a computer.
| Character Set | Character Type | Total Characters |
|---|---|---|
| JIS X 9010:1984 OCR-B Basic |
Numerals | 10 |
| Alphabets (uppercase, lowercase) | 52 | |
| Symbols, etc. | 31 | |
| Others | 3 | |
| Total | 96 | |
| JIS X 9010:1984 OCR-B Basic OCR-K |
Numerals | 10 |
| Alphabets (uppercase, lowercase) | 52 | |
| Symbols, etc. | 31 | |
| Others | 3 | |
| Katakana, etc. | 63 | |
| Total | 159 | |
| JIS X 9006:1979 OCR-HN |
Numerals | 10 |
| Others | 1 | |
| Total | 11 |
With barcodes, the characters that can be used, the character representation method, and the number of digits vary by barcode type.
| Standard | Character Set | Character Types |
|---|---|---|
| CODE39 | JIS X 0503 CODE39 basic specifications |
Numbers English upper case characters Symbols |
| CODE128 | JIS X 0504 CODE128 basic specifications |
Numbers English uppercase characters English lowercase characters Symbols |
| NW-7 | JIS X 0506 CODABAR (NW-7) |
Numbers Symbols |
| Postal services customer barcode |
Postal services customer barcode |
Symbols |
Among fonts, there are fixed-width (fixed-pitch) fonts where all characters are the same width, and there are proportional fonts where the width of each character is different.
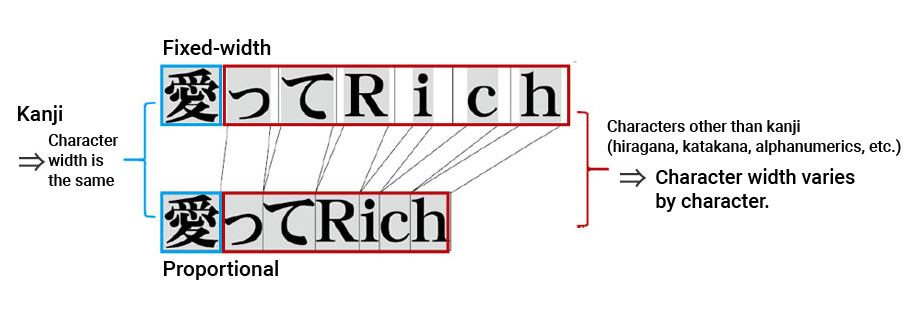
In addition, even for the same proportions, character width differs depending on the font.

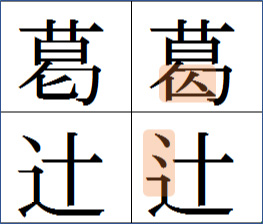
In Japanese character sets, JIS X 0208 (established 1978; revised 1983, 1990, and 1997) and JIS X 0213 (established 2000; revised 2004) exist. The character forms specified in the JIS X 0208 1990 revised edition are referred to as the JIS90 character forms and the those specified in the JIS X 0213 2004 revised edition are referred to as the JIS2004 character forms. Between the various standards, the character forms for some characters differ.
Example (left: JIS90 character form, right: JIS2004 character form)
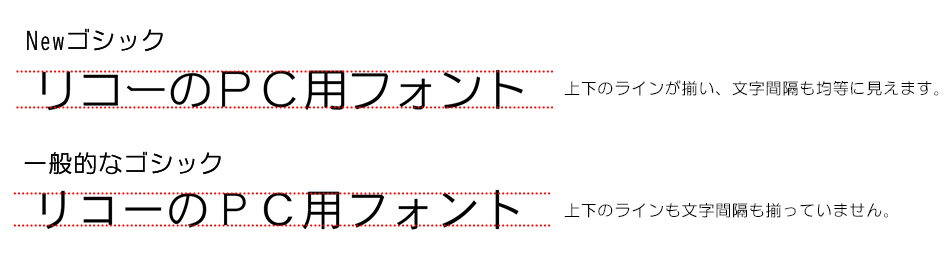
Fonts specially designed so that a wide range of people find them easy to read, easy to see, and difficult to misread are known as universal design fonts (UD fonts).
Ricoh's UD font policy
①"Easy to read"
・Adjust character height and width so that sentences can be read naturally.
②"Easy to see"
②-1:Enlarge character internal space.
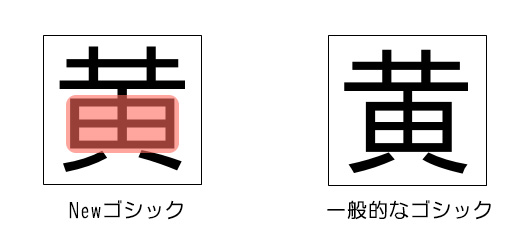
②-2:Make the differences between characters with similar forms clear.
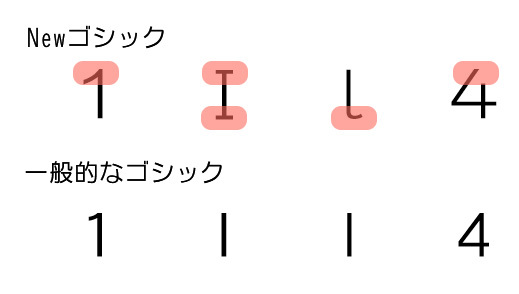
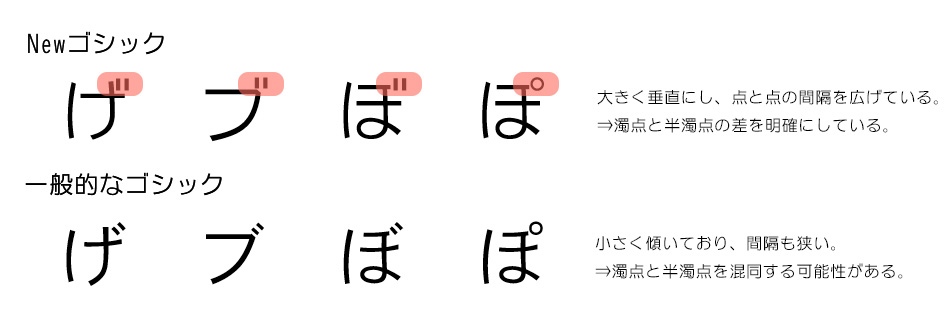
②-3:Make the difference between dakuten and handakuten clear.
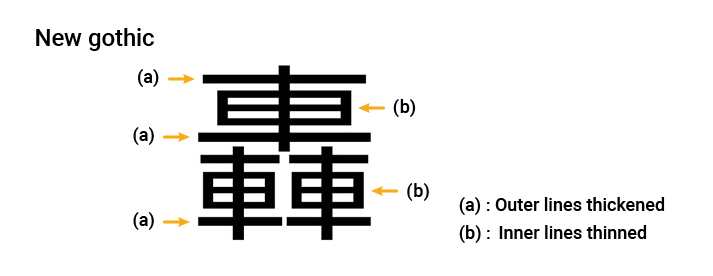
②-4:For characters with many strokes, vary the line thickness.
③"Beauty"
・Delete decorative portions to make characters simple and beautiful.
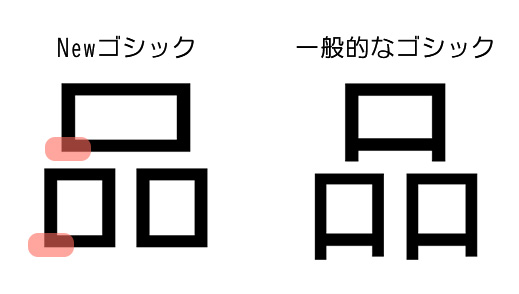
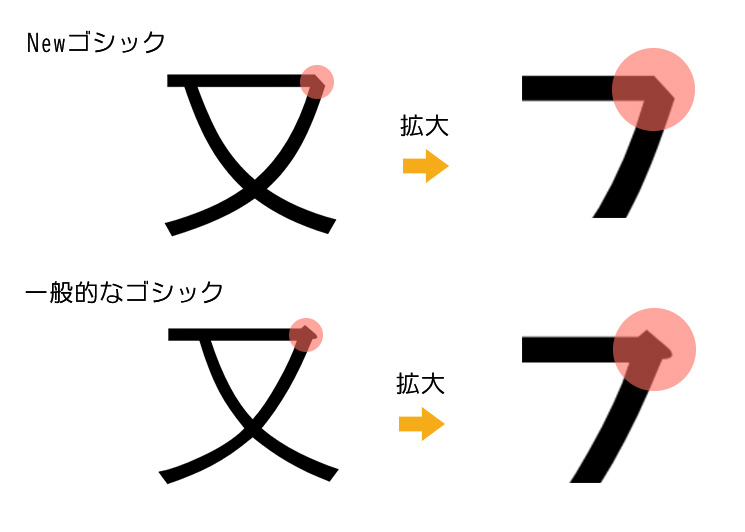
・Curved portion represented with large and gently curved line.

The term "extended characters" refers to characters not included in character sets based on the various standards (Unicode and JIS).
[When are extended characters necessary]
We recommend the use of extended characters to persons using fonts in ways such as those below.
[Mechanism for adding extended characters]
Add an extended character area within the font file
In the case of Unicode, a PUA (Private Use Area) is provided as an extended character area.
![[Mechanism for adding extended characters]](/en/-/Media/Ricoh/Sites/industry/font/general_knowledge/img/general_img16.jpg)
In the case of TrueType Fonts used in Windows®, the method shown below is also possible.
Link an extended character file (TTE format) to the font file
![[Mechanism for adding extended characters]](/en/-/Media/Ricoh/Sites/industry/font/general_knowledge/img/general_img18.jpg)
Since extended characters are added to the font file of a specific font, if the user switches to another font, the characters added as extended characters will not be displayed.
![[Mechanism for adding extended characters]](/en/-/Media/Ricoh/Sites/industry/font/general_knowledge/img/general_img19.jpg)
The term "variant character" refers to a character that has the same meaning or the same pronunciation/reading as another character but a different character form.
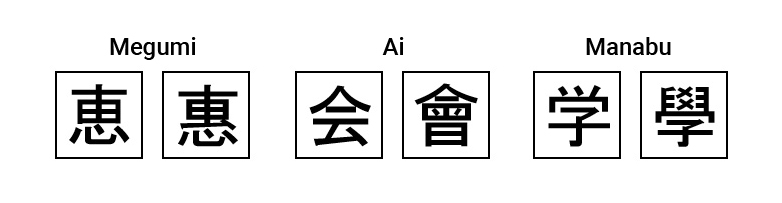
In the past, extended characters were used for the display of variant characters, but in recent years, another method has been developed.
In a font file, there may be multiple variant characters assigned the same character code, but in such cases it is necessary to have a mechanism known as IVS (Ideographic Variation Sequence/Selector) in order to differentiate how the variants with the same code are used (by specifying and displaying the character to be used).
IVS image
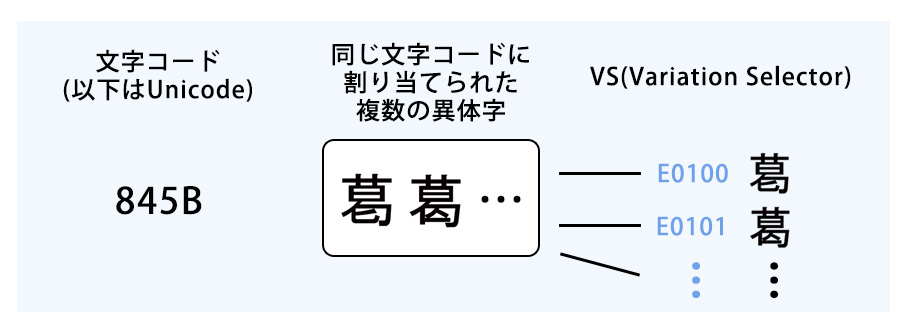
Specifically, the character forms are differentiated by adding at the back of the character code a branch number (E0100, E0101, etc.) to designate each character form.
This branch number is called a VS (Variation Selector).
When using multiple languages, it is necessary to consider the character-size balance.
European languages writing when priority is not given to the balance with the Japanese
There is the usual kind of European languages text display, but the viewer may be given the impression that there is a large
difference in character size when the text switches from one language to another.
European languages writing when priority is given to the balance with the Japanese
Ricoh has adopted this method.
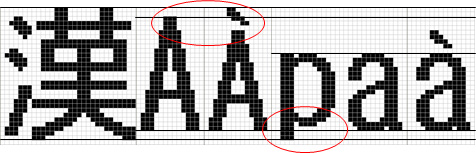
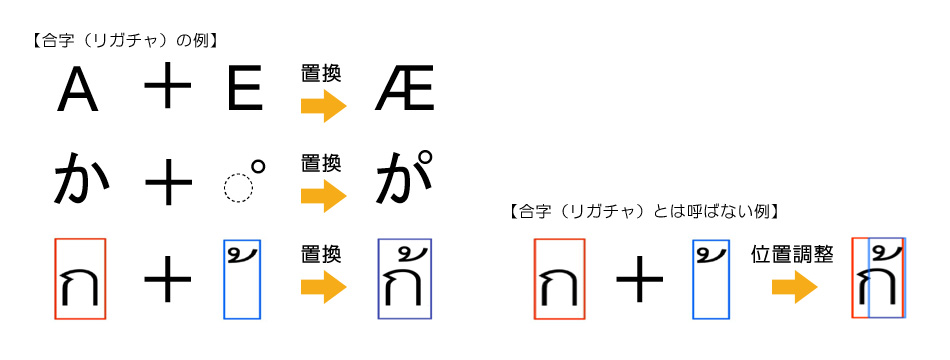
The term "ligature" refers to cases where a combination of two or more characters are replaced by a single character. This term is not used for cases where two or more characters are displayed together by adjusting their positions rather than by replacing them with a single character.
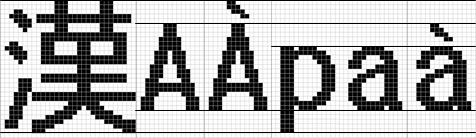
Including the Bitmap Font in the TrueType Font (and RT Font) makes it possible to prevent character illegibility by giving priority to displaying with the bitmap font using the subject number of dots.
Red characters are Bitmap Font.
| When Bitmap Font included | When Bitmap Font not included | |
|---|---|---|
| 24dot |  |
 |
| 21dot |  |
 |
| 20dot |  |
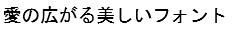 |
| 18dot |  |
 |
| 16dot |  |
 |
| 14dot |  |
 |
| 13dot |  |
 |
| 12dot |  |
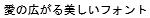 |
| 10dot |  |
 |
| 8dot |  |
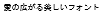 |
| 7dot |  |
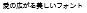 |